Vitiligo
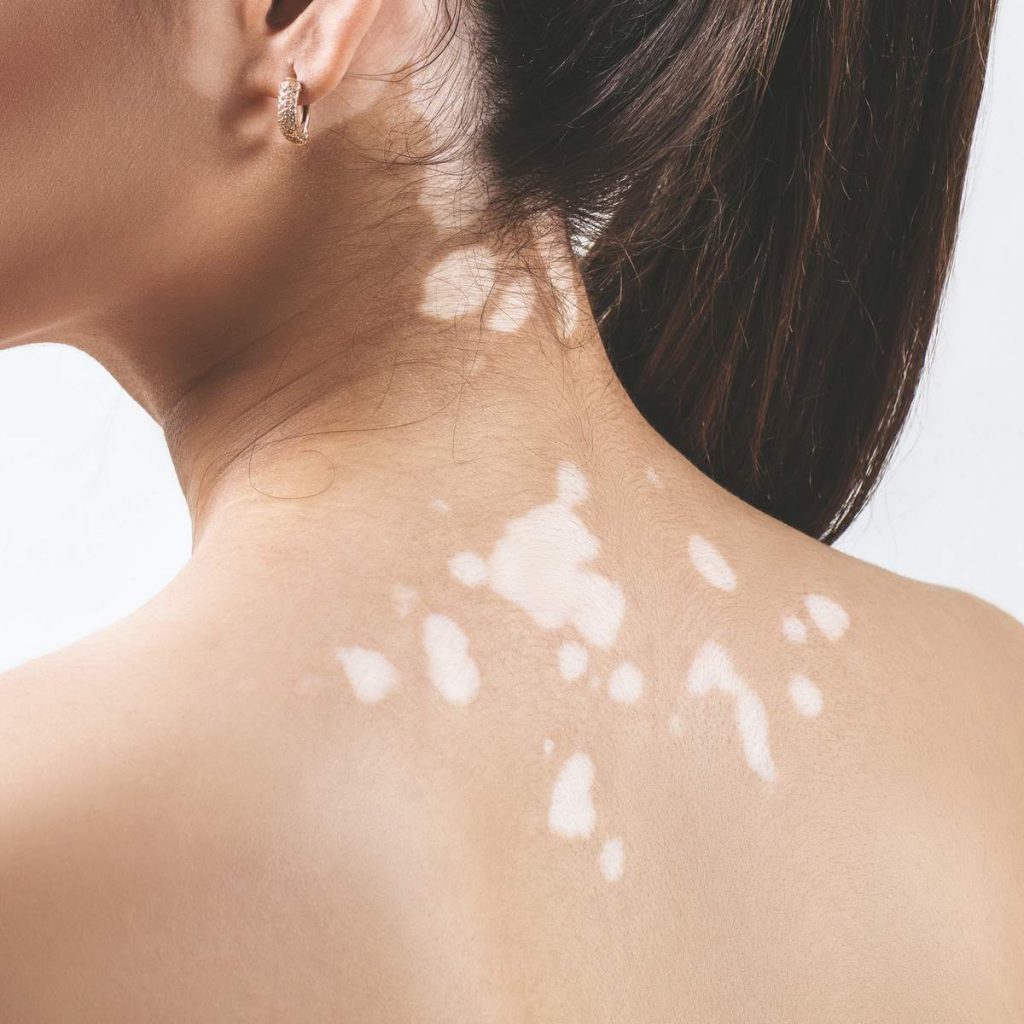
Vitiligo is a skin condition in which patches of skin loses their color.The total area of skin that can be affected by vitiligo varies between individuals. It can also affect the eyes, the inside of mouth, and the hair. In most cases, the affected areas remain discolored for the rest of the person’s life

The condition is photosensitive. This means that the areas that are affected will be more sensitive to sunlight than those that are not
It is hard to predict whether the patches will spread, and by how much. The spread might take weeks, or the patches might remain stable for months or year
The lighter patches tend to be more visible in people with dark or tanned skin.
Causes
The exact causes of vitiligo are unclear. A number of factors may contribute
- an autoimmune disorder, in which the immune system becomes overactive and destroys the melanocytes
- genetic oxidative stress imbalance
- a stressful event
- harm to the skin due to a critical sunburn or cut
- exposure to some chemicals
- heredity, as it may run in families
- a virus
Symptoms
The only symptom of vitiligo is the appearance of flat white spots or patches on the skin. The first white spot that becomes noticeable is often in an area that tends to be exposed to the sun. It starts as a simple spot, a little paler than the rest of the skin, but as time passes, this spot becomes paler until it turns white. The patches are irregular in shape. At times, the edges can become a little inflamed with a slight red tone, sometimes resulting in itchiness.
The effects of vitiligo vary between people. Some people may have only a handful of white dots that develop no further, while others develop larger white patches that join together and affect larger areas of skin.