Autologous fat
Fat grafting , also called fat transfer, plumps up facial or body features with a patient’s own fat. Fat transfer is designed to minimize wrinkles and fill in parts of the face or body with a “sunken” appearance. It can also reduce scarring and correct deformities. Since fat transfer uses your own fat cells, there is no risk of the body rejecting the tissue.
Who is a candidate?
- Facial scars, such as from acne.
- Decreased facial volume due to diseases such as Hemifacial atrophy.
- Sunken cheeks and wrinkles due to aging.
- Small, depressed areas in sections of the body—such as around the breasts.
Intended Result
Improved body contour, reduced scarring, or enhanced features.
Procedure Description
- Fat transfer is performed on an outpatient basis. Both the area from which the fat is taken and the treatment site are anesthetized with a local anesthetic.
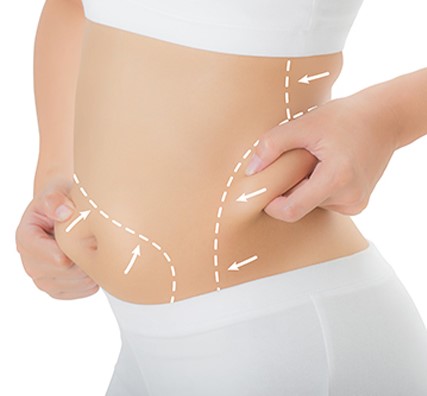
- Using a small needle, fat is removed from an area of the body where it is tightly packed, such as the abdomen or the buttocks.
- Once removed, the fat is processed to remove excess fluids and then re-injected just under the skin using another needle.
Fat Injections Procedure
A fat transfer procedure can usually be performed as an outpatient procedure at the cosmetic center of your surgeon.
Step 1) Fat Removal
The fat transfer procedure begins with liposuction to remove some excess fat from the donor site, which could be the abdomen, buttocks, hips, “saddle bags,” thighs, or even jowls. In order to collect as many undamaged fat cells as possible, only very-low-suction liposuction is used. These fat cells are removed from the donor site with a small-gauge hypodermic needle or a special cannula that is designed to limit damage to the fat cells.
Step 2) Isolating Fat Cells
Once an adequate amount of fat has been collected, it is spun at a very high speed in a centrifuge to separate the fat cells from the liquid that is also removed by the liposuction. The damaged fat cells are removed. Only whole, undamaged, and cleansed fat cells are then used for the fat transfer.
Step 3) Re-Injection of the Fat
The fat transfer procedure is completed by injecting the fat cells into the target site(s) on your face. At this point, your doctor will have already identified the site for each fat injection, with the intent to correct imperfections or create a new contour. U sing a separate hypodermic syringe, the doctor will inject the fat cells at the depth needed to achieve the desired fat transfer results.
Common areas for fat grafting include:
- Sunken cheeks
- Hollow temples
- Tear troughs
- Nasolabial folds
- Skin depressions
- Facial creases and wrinkles